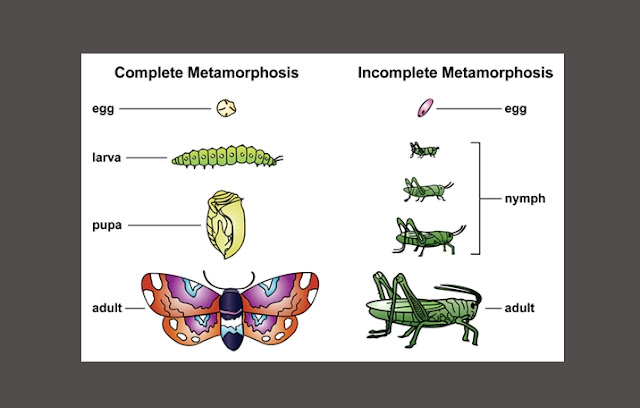
A. UNDESTANDING THE DEFINITION OF METAMORPHOSIS
Metamorphosis is the change that occurs in an
organism either structurally or functionally in the process towards maturity.
Changes in physical terms due to the growth and differentiation of cells,
whereas functional changes occur due to the development of the cells.
B. TYPES OF METAMORPHOSIS
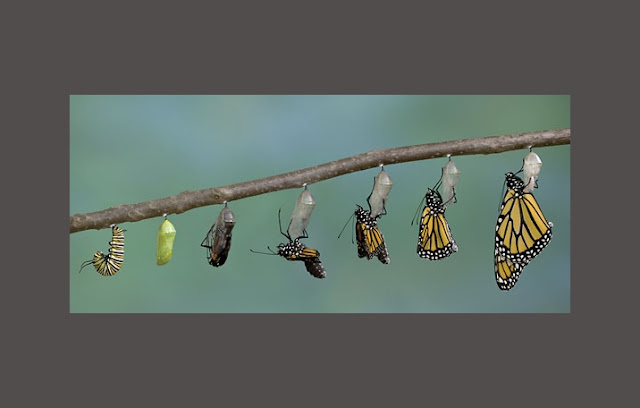
1. Complete
Metamorphosis (Holometabolous Metamorphosis)
Complete metamorphosis is a metamorphosis that make
drastic changes so that the earliest forms of organisms is very different from
its shape after metamorphosis occurs. Complete metamorphosis pass through four
stages: egg à
larvae à
Pupa à
Mature
a. Egg phase
In the egg stage, the parent of the organism will lay
eggs in a safe and comfortable place for their children. In the egg phase, embryo
fertilization of sperm and ovum will continue to make the process of cell
division that forms the main organ for life. Time that needed for this process
is different to each species, depend on the types of organism. The eggs
structure and shape also varies depending on the type.
b. larvae phase
After hatching from the egg, these organisms will get
into a larval stage. In the larval stage, he will need a lot of food for
development and growth. Therefore the place where their parents lay their eggs is
very important for the needs on this stage. A few physical changes will occur
in the larval stage, for example ;the change of skin on insect larvae, this
change will make the body ready to become a pupa. These body changes is
controlled by hormonal factors.
c. Pupa phase
At this stage, their eating habits will be reduced,
but the metabolism in the body will continue. At Pupa Phase there will be growth,
proliferation and differentiation of cells. When it is mature enough, then
these organisms will enter the mature stage.
d. Mature Phase (Adult Phase)
Adults phase is the final stage in a metamorphosis.
Usually the final form of an adult in complete metamorphosis looks very
different compare to the larvae or pupa stage. Adult phase is a “phase of
reproduction” this organism will find a partner, then mating and breeding.
2. Incomplete Metamorphosis
(hemimetabolous Metamorphosis)
Incomplete metamorphosis is a kind of metamorphosis
that is not through the pupa. Results of a mature organism that forms generally
not much different from the other stages.
a. Egg phase
Similar to the complete metamorphosis, the parent of
a living being will lay her eggs in a place that are safe and comfortable. embryo
fertilization from the sperm and ovum is protected by a strong shell. The
embryo is getting the nutrition from the components inside the egg.
b. Nymph phase
Nymph phase is the phase in which the animal is ready
to come out of the egg. Body structure at Nymph phase own a perfect form, but
in a smaller size. In this phase will occur the maturation of organs in the
body, especially the reproductive organs. At this stage also will be changes in
the structure outside the body, because of the adjustment to the increased size
of the body.
c. Adult Phase
(Mature Phase)
Same as the complete metamorphosis, at this stage all
the organs are ready to support their life. They will look for a partner to
mate later. Then fertilization results of male and female cells will enter the
early stages of incomplete metamorphosis again.