A. UNDERSTANDING THE DEFINITION OF NOSE
The nose is one of the human sensory organs and
functioning as the smell sense organ and also part of the respiratory system
that serves as the entry of air. On the nose there are smooth hairs and
receptors that sensitive to gas or vapor. When we breath, we inhale gas
substances around us so that we can feel the smell of something. The size and
shape of the nose is varied, there is a large or small size, its shape can be
flat or pointed. Usually the size and shape of the nose depends on the human
race and genetic component.
B. THE FUNCTION OF NOSE
1. As the
respiratory organs (air filter)
The nose is the first respiratory organs in the
respiratory tract, the structure inside the nose are smooth hairs, mucous, bony
walls, etc. which will serve to filter the air that enter the respiratory
tract. The nose has many blood vessels and mucus on its walls which will
function as a regulator of humidity and temperature of the incoming air, this
wall can also balance the pressure of the air by deflecting the air.
2. As the
sense of smell
The nose has olfactory nerve (the nerve of smell)
which is part of the cranial nerves (in direct contact with the brain) and
serves to respond as the stimulation agent of gases or vapors. Stimuli that
came in will be accepted by this nerve, then passed on in the form of impulses
to the brain so that we could smell something.
3. Giving taste
of food
The nose has an influence to the sense of taste that
we have, the combination of a good nose and the tongue can provide normal taste
of the foods. This effect occur because the nose is a receptor that receive the
reflection taste of the tongue. Therefore, when we are ill (flu) and
experiencing nasal obstruction, then the taste of the food will be tatesless.
4. Participate
in the voice settings
Nasal cavity resonance can affect our voice, probably
because of the influence of the incoming air pressure through the nose. When we
cover the nose, then the sound quality will be reduced compared to when speaking
in a normal state.
5. Cleaning
airways
On the nose there are mucus and enzymes that will
clear the airways from bacteria and foreign object. Additionally, when the
sneeze reflex, the foreign object in the respiratory system will issued through
the nose and mouth.
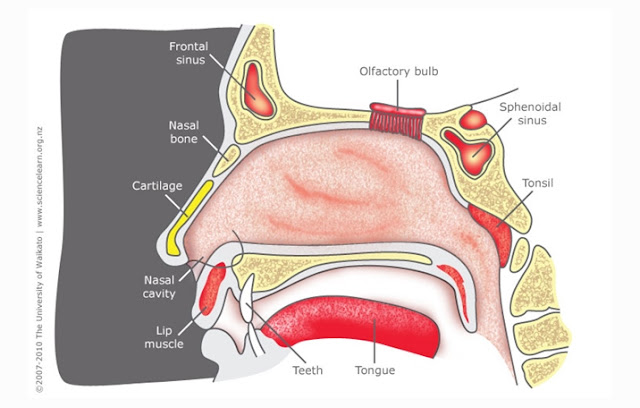
C. THE STRUCTURE AND PARTS OF THE NOSE
1. Nose Holes
Nostril is a part which serves to protect the nose
from external threats. Also plays a role in regulating the size of something
that can enter into the nose. This section relates directly to the nasal
cavity. There are two pieces of human nostrils separated by a septum.
2. Nose hairs
Nose hair is smooth hair on the nose that serves to
filter the incoming air. Nose hairs hold the dust so it can not get into the
respiratory system.
3. septum (Separator)
Nose
Nasal septum is the structure that divides the nose
into two parts. Nasal septum divides the nose into 2 parts (left and right)
starting from the nostrils to the throat. The walls of the nasal septum lined
by mucous and blood vessels that serve to moisturize and regulate the
temperature of the incoming air. The nasal septum is formed by the bones and
cartilage of the nose.
4. Nasal
Cavity
Nasal cavity is a very important organ. In the nasal
cavity are the mucous membranes and cilia (fine hair). The main function of the
nasal cavity is to continue the incoming air toward the throat. Nasal cavity
can also keep the humidity, temperature and air pressure. In carrying out its
functions, this section composed by the skull that form the walls of the nose.
There are four interconnected walls, ;superior wall (top), inferior (bottom),
medial (middle), and lateral (side).
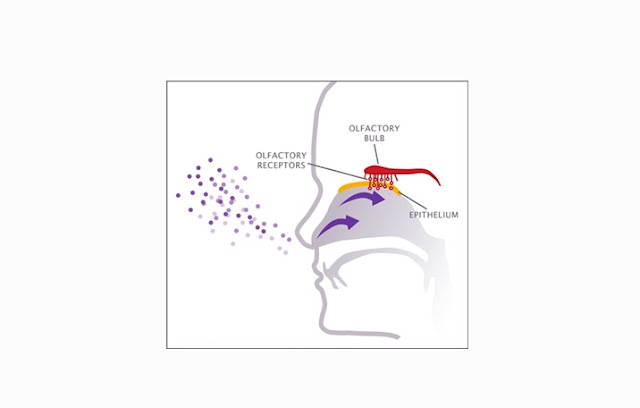
5. Nerves
(olfactory nerve)
Olfactory nerve is one of the 12 cranial nerves that
relate directly to the brain. Olfactory nerve is the first cranial nerve that
serves as the primary receptor in the sense of smell. These nerves are
stimulated in the form of odors that carried with inhaled air then transmits
that information in the form of impulses. The function of the olfactory nerve is
associated with the taste of food or the drink we consume.
6. Nasal Sinus
Nasal Sinus is a structure in the form of nasal
cavity located around the nose. Humans have four pairs of the nasal sinuses.
This structure is also known as the paranasal sinuses. All sinuses will empty
into the nasal cavity. Nasal sinuses serves to moisten and filter the air. 4 nasal
sinuses of human beings are:
- Maxillary sinus (cheekbones)
- The frontal sinus (in the middle of the forehead)
- Ethmoid sinus (between the eyes)
- Sphenoid Sinus (behind the nasal cavity)
7. Cartilage
of The Nose
Cartilage in the nose is a strong elastic structure
that is forming the tip of the nose. The shape of the cartilage that make up
the nose determine to the shape of the nose. Cartilage that forms part of the
nose called hyaline cartilage that is semi-transparent, strong and flexible.
Although it is strong and elastic, this cartilage can be damaged if the
collision is very hard.
8. Silia
The cilia are a very delicate nose hairs structures,
its main function is to perform filtration of air entering the nose.
9. Mucuos
Membrane
The mucous membranes of the nose is the part that
serves to produce extra mucus (snot) so that the nose can be shielded from dust
and bacteria.
10. Nose –
throat Connection (nasopharyngeal)
On the back of the nose there is a channel associated
with the throat known as nasopharyngeal tube. In this tube there are eustachian
tube, tonsil and adenoids (pharyngeal). Nasopharynx serves as a regulator of
air pressure by the eustachian tube (the tube connecting the ear to the throat)
and the protector of adenoid tonsil infection.
The air that is outside the body mixed with various
other gas components, including odors. The air that is inhaled from the hole
carrying chemical substances such as odors with him. This air is filtered by
the nose hairs, then chemicals are brought together will dissolve mucus in the
nasal cavity. These chemicals will be accepted by the olfactory cells that sensitive
to odor stimuli in the form of steam or gas. Information about this stimulus
will be taken by the olfactory nerve to the brain. The brain then translates
this information so that we can smell the all smell around us.