A. UNDERSTANDING THE DEFINITION OF
ERYTHROCYTE (RED BLOOD CELL)
Red blood cells are the simplest cells in the body.
Red blood cells known as erythrocytes. erythrocytesis a term derived from the
Greek, erythos which means red and kytos which means blood sheath.
Erythrocytes is part of the blood cells with the
highest number in the body whose production is different between the period of
fetal life and after birth. In the first few weeks of embryonic life, the red
blood cells of primitive nuclei are produced in the yolk sac. On the
mid-trimester of gestation, erythrocyte production was taken over by the liver
(the primary organ of erythrocyte production), spleen and lymph nodes. After
that, for about the last month of pregnancy and after birth, red cells are only
produced in the bone marrow.
The bone marrow of all bones (except for the proximal
part of the humerus (arm) and the tibia (shinbone)) will produce erythrocytes
until someone was 5 years old . The proximal part of the humerus and tibia will
only produce a little erythrocyte and then do not produce anymore when it
reaches the age of approximately 20 years. After that age, erythrocytes will be
produced in membranous bone marrow, such as the vertebrae (spine), sternum
(breastbone), costae (rib) and Illium. However, the number of red cells
produced by the bone marrow membranous will also be less and less as you are
aging.
B. THE FUNCTIONS OF ERYTHROCYTE (RED
BLOOD CELL)
Red blood cells have an important role in the body :
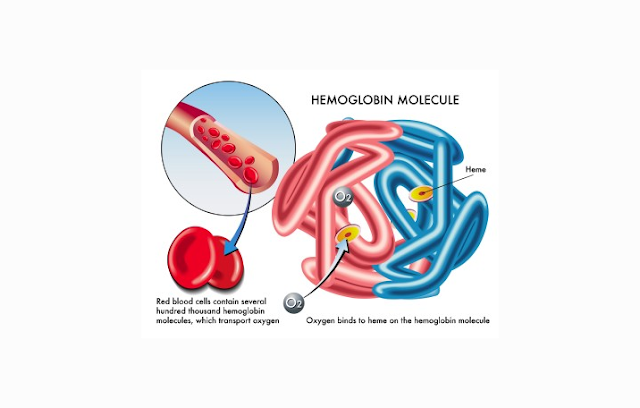
- The main function of erythrocytes is circulat blood that contains oxygen (O2) from the lungs to all of our body part. In carrying out these functions, they are assisted by the erythrocyte hemoglobin (Hb). Erythrocyte hemoglobin is a substance consisting of heme and globin chains. Heme is iron compounds protoporphyrin which form free-protein part in the Hb.
- Erythrocyte acts as a good acid buffer for whole blood.
- Erythrocytes containing the carbonic anhydrase enzyme, this enzyme increase speed in catalyzing the reversible reaction between carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) several thousand times.
- Hb as the part of erythrocyte play a role in warding off pathogens or bacteria through the lysis by removing radicals free substance that can destroy bacteria cell membranes and kill its phatogen. Therefore it is said that erythrocytes can maintaining the immune system (antibodies).
- Erythrocytes plays a role in blood vessel dilation. These can occur due to the presence of S-Nitthrosothiol compounds that released when Hb experiencing deoxigenation.
C. THE STRUCTURE OF ERYTHROCYTE (RED
BLOOD CELL)
Red blood cells are cells that have a simpler
structure than other cells. These cells have organelles such as mitochondria,
lysosomes, Golgi apparatus and the nucleus. Despite that, red blood cells are
not inert. The presence of the substance of Hb in erythrocytes gives red color
to the blood.
Normal erythrocytes have no nucleus and biconcave
plate-shaped with a diameter of approximately 7-8 micrometers with 2.5
micrometers thickness at the thickest part and 1 micrometer or less in the
middle. The shape of red blood cells can be fickle when cells walked through
the capillary, but this transformation will not cause cell rupture. This is
because under normal circumstances, red blood cells have a cell membrane to
accommodate the excess substance in it so it would not experiencing extreme
widenation.
The average volume of red blood cells in individuals
is 90-95 cubic micrometer, while the number of red blood cells rely on sex and
plains of one's home. In normal men, the average number of red blood cells per
cubic millimeter is 5,200,000 (± 300,000) and in normal women is 4,700,000 (±
300,000). People living in the highlands have greater red blood cell count than
people who live in the lowlands.
D. FORMATION OF ERYTHROCYTES
(ERYTHROPOIESIS)
The process of formation of erythrocytes is called
erythropoiesis. The formation of erythrocytes is regulated by a glycoprotein
hormone called erythropoietin. The very First cells that are recognized as the maker
of erythrocytes is proeritroblas,
formed from stem cells CFU-E. Once formed, proeritroblas cell will divide a few
times. The new cells from the first generation of the division referred to as basophilic erythroblast because it can
be painted with a base color. These cells contain little hemoglobin.
In the next division phase, the number of hb that
being formed is greater than before. Cells that are formed at that stage called
polychromatic erythroblast. On the
next stage, the amount of hemoglobin that is formed will increase and already
gives the red color to the cells. These cells are known as orthochromatic erythroblast. In the next generation, a cell has
been filled 34% of hb concentration, the nucleus condenses, and the remainder
is absorbed and eventually driven out of the cell. At the same time the
endoplasmic reticulum reabsorbed. Cells at this stage are called reticulocytes, because they contain
small amounts of basophilic material consisting of the remnants of the Golgi
apparatus, mitochondria, and few other cytoplasmic organelles.
During the reticulocyte stage, the cells will run
from the bone marrow into the capillary by means diapedesis (squeezed through
the pores of the capillary membrane). Basophilic material remaining in
reticulocytes normally disappears within 1 to 2 days, and then they turn into
mature erythrocytes. Because reticulocytes life time is short, the
concentration among all blood cells are normally less than 1 percent.
If erythrocytes are already in circulation, under normal
circumstances the life of red blood cells approximately only 120 days. Old Red
blood cells will become more brittle and can break when passing through narrow
blood vessels. Most of erythrocytes will be broken down in the spleen because
of pinched while going through the red pulp of the spleen and some other will
be dismantled in the liver. Hb that are released from erythrocyte will digested
by cells, especially macrophages in the spleen, liver and bone marrow. Later in
the liver, hb converted into bile pigment (bilirubin), which will be
accommodated in the gallbladder. Bilirubin function is to gives color to the
stool. Iron that contained in hb transported later transported into the bone
marrow to be used in the formation of new red blood cells or stored in the
liver and other tissues in the form of ferritin.
In the formation of erythrocytes, O2 levels in the
air, the hormone erythropoietin, a protein, cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), iron (Fe)
and vitamin B12 is important, because it is the factors that can affect that
process.