A.THE PURPOSE OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING
THINGS (ORGANISMS)
- Simplify the biodiversity to be easily studied.
- Providing the characteristics for living beings to be able to distinguish each type.
- Grouping the living creature according to the basic classification.
- Describe the relationship (correlation) between a living organism to another.
 |
| CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS (ORGANISMS) |
B. BENEFITS OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING
THINGS (ORGANISMS)
- It's easier to get information through the grouping of living things.
- Can distinguish the types of living things based on their characteristics.
- Knowing the relationship (correlation) between living beings one to another.
C. BASIC CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
(ORGANISMS)
Grouping of living creatures do by reviewing specific
basis. Basic classification is the rule to form a group that suits your needs.
Some basic classifications are :
- Based on Morphology and Anatomy of the body, grouping the living beings based on their structure, function, and shape. For example, tigers and cats have a similar body shape, so based on morphological body then they will be in the same classification group.
- Based on Environment, grouping the living beings based on the ground where it grows and develops. For example, fish and jellyfish are from the sea, then by the environment in which their lives, they will be in the same group.
- Based on the Similarities and Differences, Grouping of living organisms by comparing them with each other to obtain on their similarities and differences.
- The food based types, grouping the living beings based on their food. There are living beings who eat meat, and those who eat plants. For example, goats and cows, they both eat grass, then based on their type of food, then they will be in the same group.
There are still a lot of grouping system can be used
to perform the classification of living things. Therefore scientists pinpoint
the basic standard that can be used internationally. This classification system
called hierarchical Taxon (Taxonomy Levels).
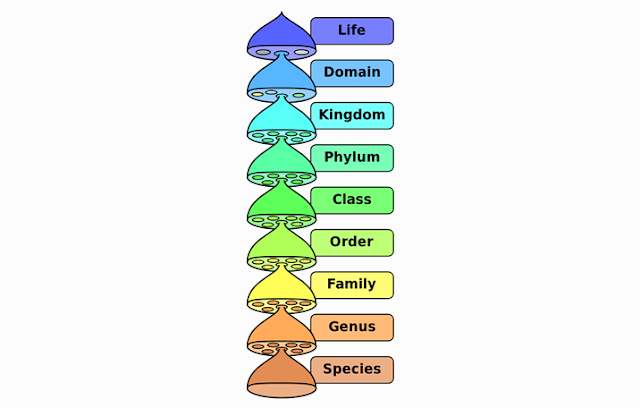
D. CLASSIFICATION
OF LIVING THINGS BASED ON TAXONOMY LEVELS
The higher their position in Taxonomy level, the more
members it has, but there are still many differences between members of the
same taxon. Here are the Taxonomy level from the highest to the lowest.
1. Kingdom
(kingdom)
Kingdom is the highest level with the most members.
There are differences in the classification of living things in this levels.
However, each group has a legitimate basis of classification. Here are several
classifications kingdom known:
- 2 Kingdom Classification, Living organisms are divided into two major groups namely the Animalia Kingdom (Animals) and the Plantae Kingdom (plants).
- 3 Kingdom Classification, Living organisms are divided into 3 groups: Animalia Kindom (Animals), Plantae Kingdom (plants), and Protists Kingdom (unicellular living creature or a simple multicellular).
- 4 Kingdom Classification, living beings are categorized into four groups, the Animalia Kingdom (Animals), Plantae Kingdom (plants), Protists Kingdom (eukaryotic microorganisms [have nuclear membrane] are not included in the group animalia or Plantae), and the Monera Kingdom (living creatures that do not have a nuclear membrane and generally unicellular).
- 5 Kingdom Classification, Living organisms are divided into five groups, namely the Animalia Kingdom (Animals), Plantae Kingdom (plants), Protists Kingdom (microorganisms eukaryotic [have nuclear membrane] are not included in the group animalia or Plantae), Monera Kingdom (Creatures that does not have a nuclear membrane), and the Fungi / Mycota Kingdom (Mushrooms).
- 6 Kingdom Classification, Living organisms are divided into 6 groups, namely the Animalia Kingdom (Animals), Plantae Kingdom (plants), Protists Kingdom (microorganisms eukaryotic [have nuclear membrane] are not included in the group animalia or Plantae), Fungi / Mycota Kingdom ( mushrooms), Eubacteria Kingdom and Archaebacteria Kingdom.
- 7 Kingdom Classification, Creatures categorized into 7 groups, namely the Animalia Kingdom (Animals), Plantae Kingdom (plants), Protists Kingdom (microorganisms eukaryotic [have nuclear membrane] are not included in the group animalia or Plantae), Chromista Kingdom (Members are a kind of living creature fungi and protists that can not be included in that group), Kingdom Eumycota (True Mushrooms), Eubacteria Kingdom and archaebacteria Kingdom.
 |
| CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS (ORGANISMS) |
2. Phylum or
Division
Phylum word used in the taxonomic level for the
animals, while Division used for the taxonomic level in plants. Phylum word
comes from the Greek meaning "branch". So it can be interpreted that Phylum
is a branch of Kingdom levels. Grouping at this stage based on the structure,
characteristics and lineage of an organism. Examples of phylum are echinoderms
(marine animals with spiny skin) and Platyhelminthes (flatworms), While the
examples of Division in plants is Bryophytes (Mosses), Pterydophytes (Vascular
Plants), and Spermatophytes (seed plants).
3. Class
(Class)
Members of the phylum level taxon and division
divided based on certain characteristics. The result is a group called Class.
Names of members of classes using different suffixes to be more easily
recognizable. Some of them are with the suffix: -phycae (Algae), -Opsida (moss),
and -edoneae (Closed Seed Plants). For example, the Division Bryophytes divided
into three classes, namely Hepaticopsida (Heart Moss), bryopsida (Leaves Moss),
and Anthoceratopsida (Horn Moss).
4. Ordo
(Order)
The Order is below the level of the class (Class).
Grouping the order based on the characteristics that more specific. Name order
in plants is usually terminated by -ales. Examples Dycotilenae classes are
divided into several orders Solanes, cucurbitales, malvales, Rosales, Poales,
and Asterales.
5. Familia (The
Tribe)
Members of every order is further divided into
smaller groups called Familia (Tribe) based on their characteristics. Familia
names in plants generally use the suffix -aceae while the animal is usually
terminated by -idae. Human familia called Homonidae.
6. Genus
Genus is a Taxonomy levels that is smaller than the Familia
(Tribe). Same as before, members of this level are grouped with the more
specific characteristics. The genus name consists of one word, and the first
letter must be written in capital letters and all letters must be italicized or
underlined.
7. Species
The species is the lowest level in the taxonomy
levels. Members of this level have almost equal characteristics with each
other, even sometimes the biologically marriage between two different species
can produce a new species. Name of the species consists of two words. The first
word indicates the genus name while the second word indicates specifications.