A. UNDERSTANDING THE DEFINITION OF BONE
Bone is strong and resilient organs that give shape
to the body. Boneless body will not be able to stand upright. Bone also serves
in the motion system. In everyday life people are always doing the motion
(movement). System of motion in humans is supported the two main components :
bone and muscle. Muscle is called active locomotor and bone is called passive
locomotor. The bone is a passive tool movement because they can not move
themselves, but must be driven by muscle.
B. THE FUNCTIONS OF BONE
Eac Bone has a different shape. So the bone will
function according to their shape. Here are some of the functions of human
bones.
- Supporting and giving body shape
- Protector of the vital organ of the body such as the brain, heart, lungs etc.
- Composer skeleton
- Where the muscles attach
- Points formation of blood cells
- Storage of minerals (potassium and phosphorus)
C. TYPES OF BONE
Based on its constituent tissue, bone can be divided
into two kinds : cartilage (soft bones) and hard bones (osteon).
1. The
cartilage
When you hold the ear or nose tip, you can feel
supple area. Why is that? Concha and the nasal tip feels supple because it was
formed by cartilage.
Baby in the womb is almost entirely composed of
cartilage. Cartilage will develop into hard bone, although not entirely. So
that in adults, the cartilage is only found in certain places, such as earlobes,
tip of the nose, larynx, trachea, bone joint surface, between the ribs and
sternum, and between the segments of the spine.
Cartilage is formed by cartilage cells (chondrocytes)
and matrix (base material). Cartilage can be divided into three kindsv : hyaline
cartilage, elastic cartilage and fibrous cartilage.
- Hyaline cartilage, is smooth, transparent, and has a homogeneous matrix. Hyaline cartilage can be found on the surface of the joints and the tracheal wall.
- Elastic cartilage, is flexible and elastic, matrix containing fibers branching. Elastic cartilage found on the tip of the nose and earlobes.
- Fibrous cartilage, is less flexible and contains many fibers of collagen matrix. Fibrous cartilage can be found between vertebrae segments and cartilage in the knee (tendons and ligaments).
2. Bone (osteon)
In contrast to the cartilage, the hard bone is composed
by bone cells (osteocytes). Bone cells secrete matrix containing calcium and
phosphorus so that bones become hard and inflexible. Bone matrix is not solid
and has hollow-empty cavity to form spongy bone. Most of the hard bone will
draw up the framework of the body.
D. SHAPES OF THE BONE
Based on the shape, bone can be divided into four
types : short bones, long bone, flat bones and irregular bones.
1. Long Bones
It has a shape like a hollow tube. Long Bones can be
found in the femur, fibula, ulna, tibia, and lever.
2. Short bones
It has a shape like a cube. This bone is only found
at the base of the foot, armpit, and the joints of the spine.
3. Flat Bone
As the name suggests, this form of the bones is flat.
Flat bone serves as constituent or protector of a cavity in our body. Examples
of flat bones are ribs, scapula, and skull.
4. Irregular
Bones
Bones that have irregular shapes. Irregular bones can
be found in the bones of the face and spine.
E. STRUCTURE OF THE BONE
Long bones such as the femur consists of two
different structures : compact bone (cortical) and spongy bone (cancellous or
trabecular). Compact bone form a solid cylinder on the central axis of the bone
surrounding the bone marrow cavity. Accounted for 80% of bone mass in the human
body is Compact Bones. Spongy bone located at the ends of long bones, accounted
for about 20% of total bone mass and has a structure like a beehive.
Bone itself is made up of 10-20% water, about 60-70%
mineral and the rest is collagen (Collagen is a major fibrous protein in the
body), but bone also contains small amounts of other substances such as
proteins and inorganic salts. The composition of the mineral component of bone
form as hydroxyapatite (HA) which is a combination of calcium and phosphate,
with the chemical formula CA10 (PO 4) 6 (OH) 2.
At the ends of the bones, there are an extension pipe
function to connect on bone with another bone. The wide end of the bone which
is composed of spongy bone called epifise.
Mid section which extends between that wide end called diafise, its a compact bone containing a cavity called the bone
marrow cavity. Between Diafise and epifise is an area called epifise chakras.
Epifise chakra area is growing from time to time as long as someone is still
growth.
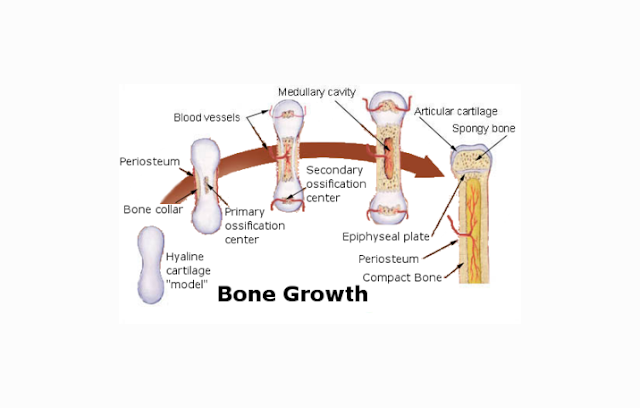
F. FORMATION OF BONE
In the stage of embryonic development, our body is
still a skeleton of cartilage. Cartilage is formed by the cells of the
mesenchyme. In cartilage will be filled by osteoblasts. Osteoblast is A
bone-forming cells. Osteoblasts will fill the surrounding tissue and form
osteocytes (bone cells) .Bone cells is form concentric shapes (from the inside
to the outside), each bone cells will surround the blood vessels and nerve
fibers, create a system called Havers systems. Bone also has osteoclasts, These
cells function is to reabsorb bone cells that have been damaged and destroyed.
The existence of these osteoclast cell activity can causes bones to be hollow.
This cavity will eventually be filled by the bone marrow.
 |
| FORMATION OF THE BONE |
The process of bone formation is called ossification.
The process is divided into two : intramembranosa ossification and intracartilagenosa
ossification. Intramembranisa ossification also known as direct (primary
ossification). This process occurs in flat bones such as the skull.
Reinforcement is only done once and will not be repeated forever. And the
example of intercartilagenosa is the formation of long bone that will increase
bone length.




