A. UNDERSTANDING THE DEFINITION OF
MEDULLA OBLONGATA
The brain is divided into five sections, namely a
Cerebrum and cerebellum, midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata. Under the
cerebellum are pons which serves as the respiratory center. Well, under the
pons, there is an organ called the medulla oblongata.
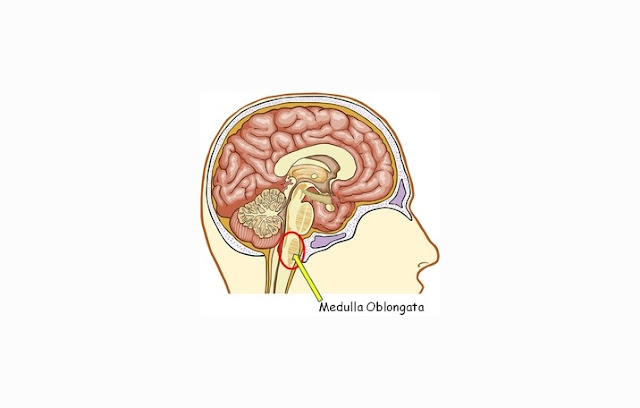
Medulla oblongata is one part of the brainstem that
are Located under the pons. Medulla oblongata itself plays a role in
controlling the functions of the autonomic (involuntary functions) system such
as breathing, digestion, heart rate, vascular function, as well as swallowing
and sneezing.
Medulla oblongata is also an organ that can deliver
signals from the brain before it is submitted to the nerves in the spine
(spinal cord). Therefore, the medulla oblongata is a very important organ in
the human body.
B. THE STRUCTURE OF MEDULLA OBLONGATA
Medulla oblongata (Cord marrow / cord connection) has
some structure / part which has the characteristics and duties of each, these
sections are:
1. Descending Tract
Descending tracts are neural pathways from the brain
and pass through to the medulla oblongata and the to the spinal cord.
Descending tract functions is to carry impulses (signals) received from brain
nerve to be delivered to the spinal cord before continuing to the organs of the
body.
2. Ascending
Tract
Ascending tract is the opposite of the descending
tract. If the descending tract comes from the brain, the ascending tracts
coming from the spinal cord, and serves to carry impulses (signals) from the
organs through the spinal cord, and pass through the medulla oblongata then to
the brain.
3. Spinal
Nerves Nucleus
There are three nucleus (core) nerve in the medulla
oblongata, the hipoglossus nucleus (which is the core of the nerve to innervate
part of the tongue), motoric dorsal nucleus of the vagus (to control the
motoric movement) and the nucleus of the solitaries tract.
C. THE FUNCTIONS OF MEDULLA OBLONGATA
As mentioned before, the medulla oblongata plays a
role in controlling the body's autonomic functions such as breathing rhythm
control, set the rhythm of digestion, regulate heart rhythm, regulates the
function of blood vessels, and others. These functions are influenced by
several unique receptors located throughout the body and will react to
environmental changes. For example, the chemoreceptors in the lungs that will
send information to the medulla oblongata when the body is exercising, the medulla
oblongata will send a chemoreceptors that improve the body's oxygen uptake in
order to survive in this situation. These kind of receptors will control
medulla oblongata in order to regulate the respiratory rhythm in accordance
with the condition of the body.
There are a lot of medulla oblongata’s function that
we still dont know. But for sure, here are some of the functions of the medulla
oblongata :
- As a connection between the brain and spinal cord
- Regulate the body's reflex
- Stimulate thirst
- regulate emotions
- Responsible for some of autonomic function
- Affect hormone production in the pituitary gland in the brain
- Controlling bed activities
- Controlling the diameter of blood vessels, widened or narrowed in accordance with the state of the body
- Detect the degree of acidity of the blood
- As a central regulator of heart rate
- Assist breathing rhythm
- Regulate blood circulation
- Regulates body temperature
How Does
medulla oblongata works ?
1. Parts of Medulla
oblongata that serves as the respiratory center:
Dorsal Group, the nervous system that forms the
automatic breathing.
Ventral Group, a group of nervous system which
innervate the muscles of respiration
2. The medulla
oblongata as regulator of the Heart
Cardioaccelerator Center, which works to increase
heart rate and strength of heart contractions
Cardioinhibitori Center, which works to reduce heart
beat to the vagus nerve (parasympathetic nerve)
3. The medulla
oblongata as Vasomotor Center
Medulla as vasomotor means that medulla serves to
control the diameter of our blood vessel function through sympathetic nerves in
the measurement of blood pressure
4. The medulla
oblongata as Non-Vital Reflex Center
In this case, the medulla oblongata function is to
regulation of swallowing, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, choked.
D. MEDULLA OBLONGATA CIRCULATION SYSTEM
Medulla oblongata is just like other organs in the
human body, it has a special blood vessels that carry blood to the medulla
oblongata itself. There are several branches of the blood vessels that circulate
medulla oblongata, which are:
1. Anterior Spinal
Artery
These arteries supplying blood and nutrition for
almost all part of meudulla oblongata.
2. Posterior
Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA)
This artery is a major branch associated with
anterior spinal artery. These blood vessels provide blood supply to the back
side (posterolateral) of medulla oblongata.




1 komentar
I am looking for some good blog sites for studying. I was searching over search engines and found your blog site and this really amazing site.
https://blog.mindvalley.com/medulla-function/